

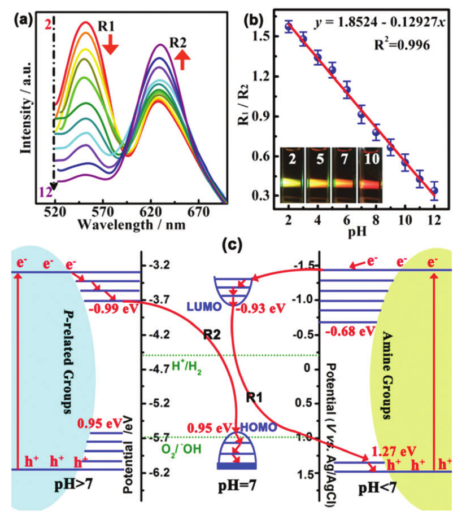
Fluorescent carbon dots (CDs) have attracted increasing attention in recent years owing to their most significant advantages in terms of low toxicity, resistance to photobleaching, small size, easy functionalization, eco-friendly synthesis and diverse imaging capabilities. However, the unclear optical mechanism of CDs greatly limits their further application. Understanding the optical property of CDs is of great significance for controllable development of top-designed CDs with functional purposes. In this review, we firstly summarize that light absorption properties of CDs, and demonstrate the relationship between the absorption spectrum and electron transition of both the core and shell of CDs. Furthermore, we summarize the common fluorescent mechanisms of CDs, including surface state, quantum confinement effect, conjugated structures, self-trapped excitons, edge defects, free zigzag sites, and multi-emissive centers. Finally, we also discuss the phosphorescence properties of CDs. This review gives new insights into how to tune the fluorescence and phosphorescence of the CDs.

Scheduled Server Maintenance and System Downtime Notice Dec 16, 2025
Celebrating CM Editorial Board Members Recognized in the Wor... Oct 10, 2025

Food Science and Engineering Now Indexed in CAS Database Aug 20, 2025

Contemporary Mathematics Achieves Significant Milestone in 2... Jun 19, 2025

Three Journals under Universal Wiser Publisher are Newly Ind... Apr 21, 2025